Normal Fetal Urinary System Ultrasound
Page Links: Transverse Views Kidney, Coronal Views Kidney, Renal Arteries, Fetal Bladder
Contribution to images: Jane J.K. Burns, A.S., R.T., RDMS.
Introduction
The kidneys can be visualized as early as 9 to 12 weeks gestation, especially with transvaginal ultrasound. Urine production starts by 10 weeks gestation [1] but is not a significant contributor to amniotic fluid volume until 15 weeks or greater. At 18 to 20 weeks, the kidneys are slightly hyperechoic compared to the surrounding tissues including the fetal bowel. [2] The renal pelvis is seen as an echo free area and the ureters are not normally visualized. As the pregnancy advances, the renal echogenecity increases and during the last trimester, the kidneys are surrounded by peri-renal fat while the pyramids are echopenic. The bladder is identified as an echo free structure in the central pelvis and should always be observed during the second and third trimester.
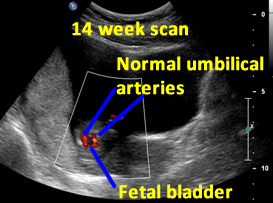
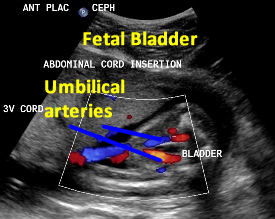
Above. Patient A. 14 weeks gestation. The fetal bladder and the umbilical arteries around the bladder are identified.
Transverse Views Kidney
Above. Patient B. 20 weeks gestation. Classic transverse view with spine dorsal position and kidneys well defined. The renal pelvis is 2 mm. in the anterior posterior (AP) diameter, which is within normal limits. Cursor placement is inner to inner as demonstrated.
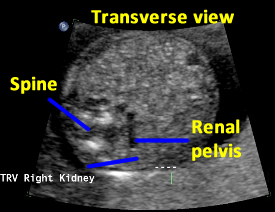
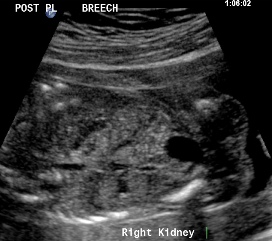
Above. Patient C. 18.2 weeks gestation. Transverse view. The spine is now lateral and inferior to the classic dorsal position, but the right kidney is well imaged in this position.
Above. Patient C. 18.2 weeks gestation. Transverse view. The spine is again lateral and inferior to the classic dorsal position. While the kidney is inferior to the spine, visualization is acceptable.
Above. Patient D. Transverse view. Mid-trimester. The renal outline appears circular and the renal pelvis is well defined.
Coronal Views Kidney
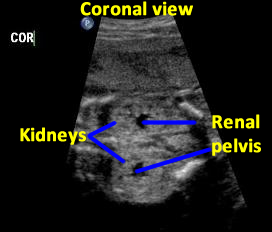
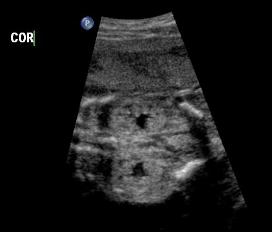
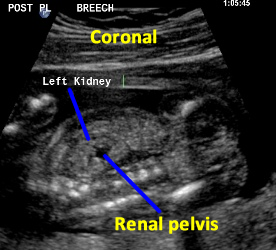
Above. Patient C. 18.2 weeks gestation. Coronal view. Both kidneys can be imaged and measured in this plane. The renal pelvis is seen, is symmetrical, and measures within normal limits in the AP diameter.
Above. Patient C. 18.2 weeks gestation. Coronal view. Each individual kidney can also be measured in this plane.
Above. Patient C. 18.2 weeks gestation. Coronal view. Again, each individual kidney can also be measured in this plane.
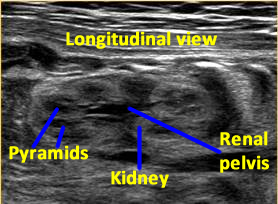
Above. Mid-trimester. Longitudinal view. The kidney is well outlined, and the normal renal pelvis is visualized.
Above. 33 weeks gestation. Renal pyramids are echopenic. Peri-renal fat outlines the kidney and the renal pelvis is normal.
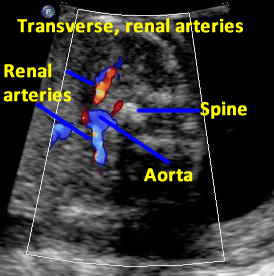
Renal Arteries
Above. Patient D. 20 weeks gestation. Transverse to oblique view. Color Doppler of the renal arteries.
Above. Patient E. 20 weeks gestation. Coronal view. Color power Doppler of the renal arteries.
Fetal Bladder
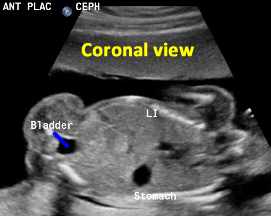
Above. Patient F. 20.2 weeks gestation. Coronal view with the fetal bladder in relationship to the rest of the intra-abdominal organs.
Above. Patient G. 19 weeks gestation. Coronal view. Again, with the fetal bladder in relationship to the rest of the intra-abdominal organs.
Above. Patient F. 20.2 weeks gestation. Umbilical arteries entering into the umbilical cord after coursing their normal anatomic position outlining the fetal bladder.
References
Twining, P., Genitourinary malformations. In Diagnostic Imaging of Fetal Anomalies. Nyberg, DA, et al, eds. Lippincoit, Williams, and Wilkins. 2003. PP: 604-05. Twining, P., Genitourinary malformations. In Diagnostic Imaging of Fetal Anomalies. Nyberg, DA, et al, eds. Lippincoit, Williams, and Wilkins. 2003. PP: 604-05.
1
2